How To Open Activity Monitor Windows
Activity Monitor is the Mac equivalent to the Windows Job Manager. It displays a diverseness of resource in use on your organization in real time. These include processes, deejay activity, retentivity usage, and more to provide a sort of dashboard into what's going on in your Mac.
We'll show y'all how to read and use Action Monitor for Mac. You lot'll also acquire how CPU, RAM, and deejay action can affect your Mac's functioning over fourth dimension.
How to Open Activity Monitor on a Mac
The Activity Monitor app lives in Applications > Utilities. To open up it, press Cmd + Space to launch Spotlight. Then type in the first few letters of the app and press Return when Action Monitor appears at the pinnacle of the list. However, there are diverse other means to open and interact with the Mac resource monitor. Here's our guide on opening the task manager on a Mac.
In the Activity Monitor, in that location are five system monitor indicators that give y'all the existent-time stats and graphs of resource usage over time. The data might be useful to troubleshoot problems on your Mac. We'll detail each of these options below.
1. Monitor the CPU With Activity Monitor
The CPU tab shows how every process uses your figurer's processor. Y'all'll see what percentage of the total CPU a process is using (% CPU), how long information technology's been active (CPU Fourth dimension), the number of times a process awoke from the sleep state (Idle Wake Ups), and more than.
At the bottom of the screen, you lot'll also see the percentage and graph of your CPU used past the Arrangement (red) and User (blue).
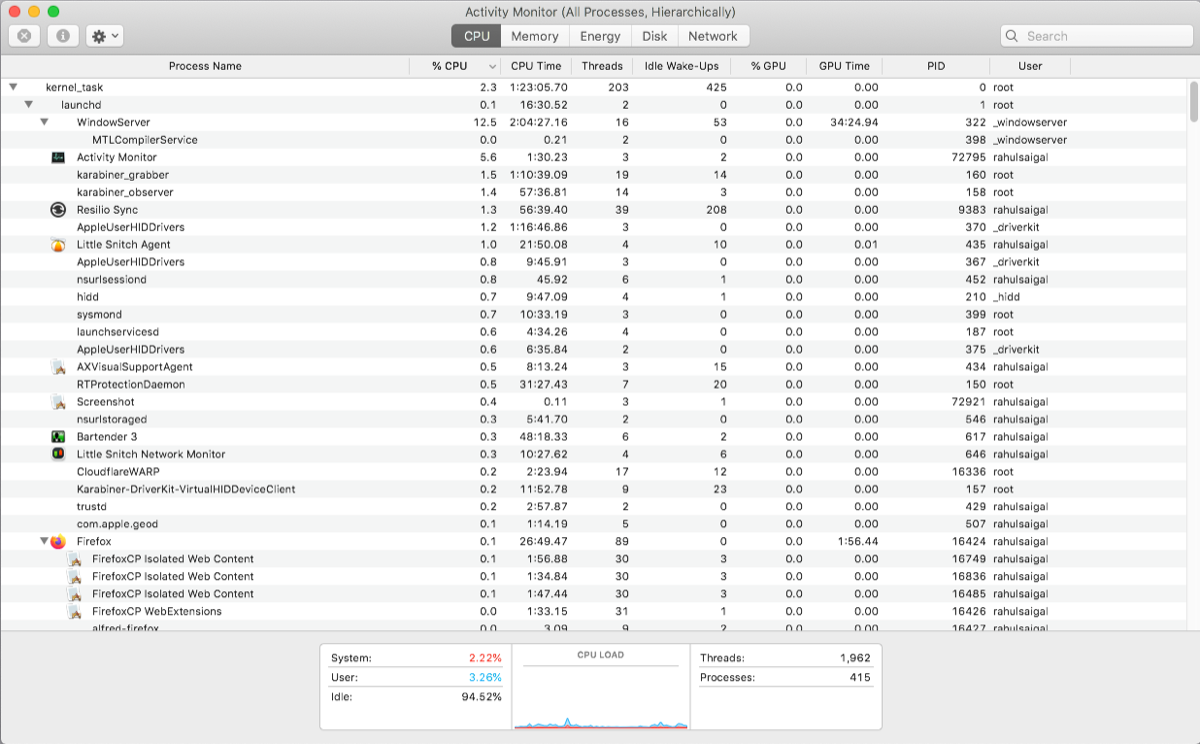
List Processes by %CPU
To see which processes are consuming excessive resource, choose View > All Processes and click on the % CPU column to sort them by usage. Some processes may occasionally display high CPU usage, merely that doesn't necessarily indicate a problem. For case:
- The mds and mdworker processes associated with Spotlight might show frequent CPU spikes during indexing. This is perfectly normal for a new or recently formatted Mac. The process volition end automatically when done.
- The kernel_task process manages your Mac'south temperature by limiting CPU access to processes that apply the CPU intensely. It's common to see this consume more than CPU over time. Thankfully, yous can ready "kernel_task" high CPU usage on your Mac.
- A web browser may show high CPU usage while rendering too many tabs or displaying multimedia content similar video.
- Cloudd is the daemon procedure that deals with syncing iCloud data. If you come across a fasten in CPU usage, this doesn't point a problem. One time the syncing completes, the %CPU should go reduced.
View CPU Usage and History
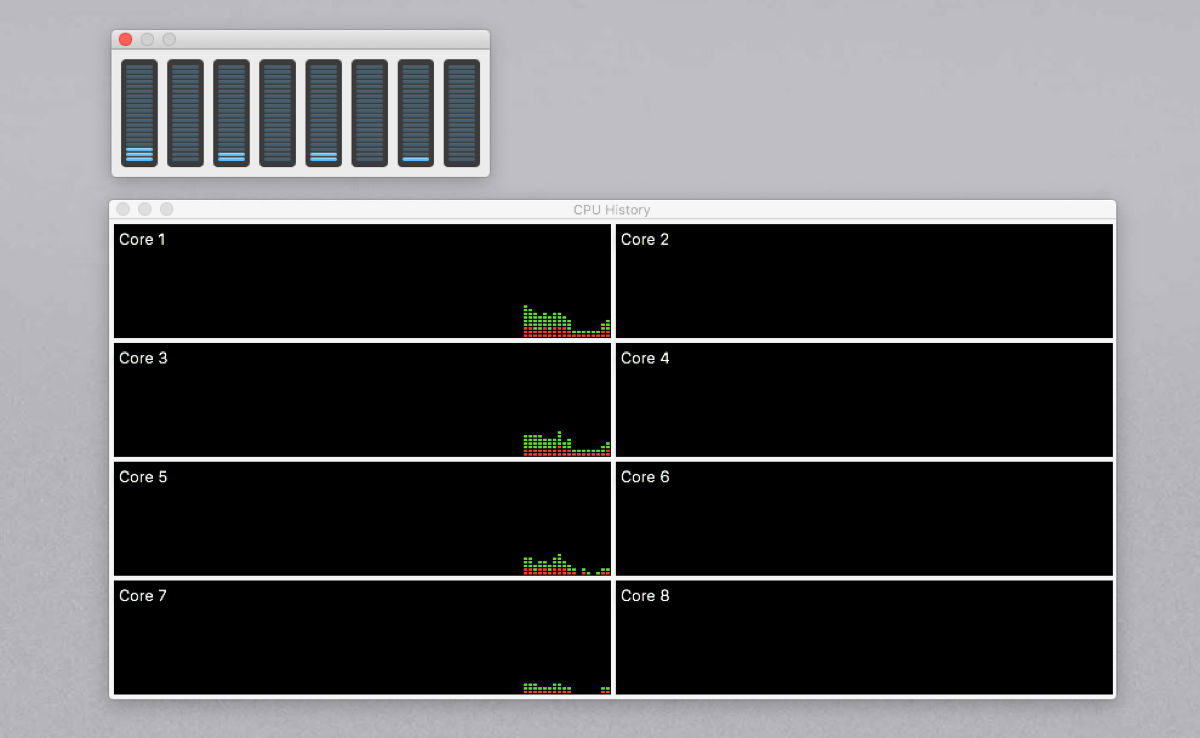
Click the Window menu to open CPU Usage, CPU History, and GPU History in a split up window. The information will give you insights into your overall CPU utilization. The CPU History window shows user and arrangement load on each core over time.
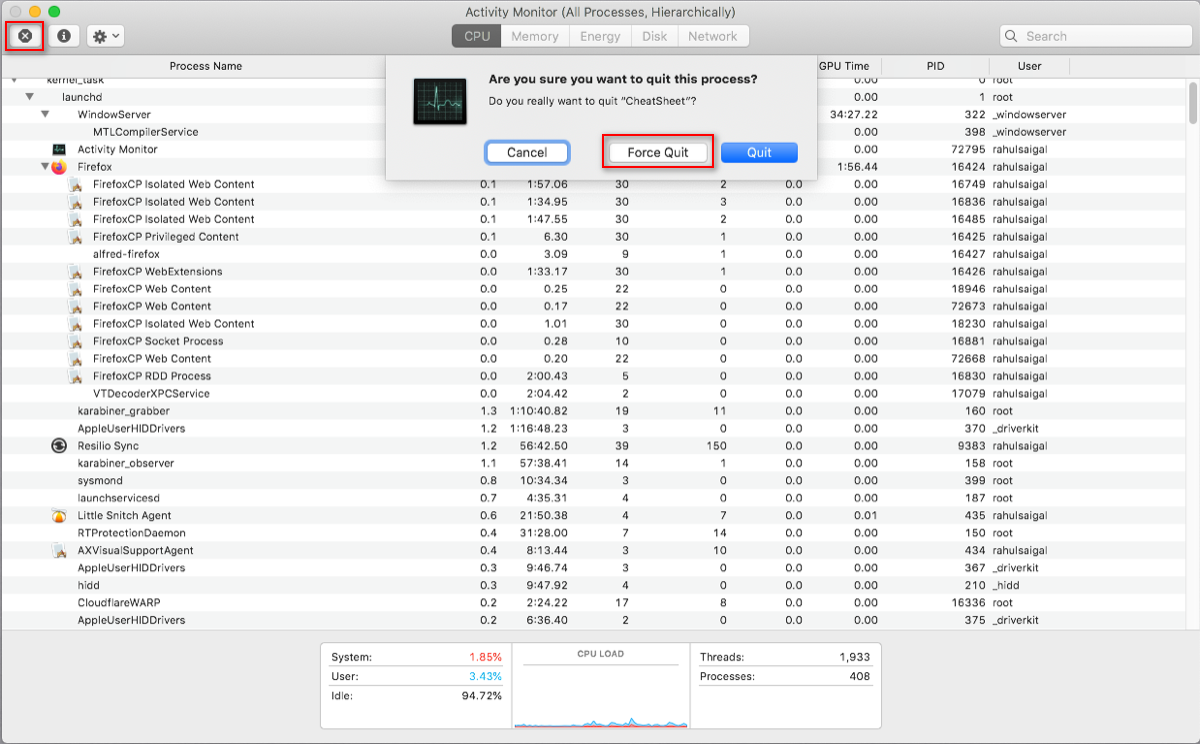
Quit Rogue Processes
If an app is interim weird, becomes unresponsive, or crashes, then your all-time choice is to force quit it. Yous'll encounter the problematic processes in red text with the phrase Not Responding.
To finish the process, select the app and choose View > Quit Procedure. Or click the 10 push button at the top of the toolbar to quit the process.
If Activity Monitor is not working, try these culling steps:
- Press and hold Cmd + Selection + Esc. Choose the app you want to quit in the Forcefulness Quit Applications dialog box and click Force Quit.
- Open the Terminal app.
- Type the following command:
>ps -ax - Printing Return to list all the running procedure forth with PID (Process Identification) number. To force quit an app, type
>kill <PID number>
- Type the following command:
You should never forcefulness quit system processes or ignore processes that run equally root. Instead, notice out the probable cause by looking at logs or restart your Mac.
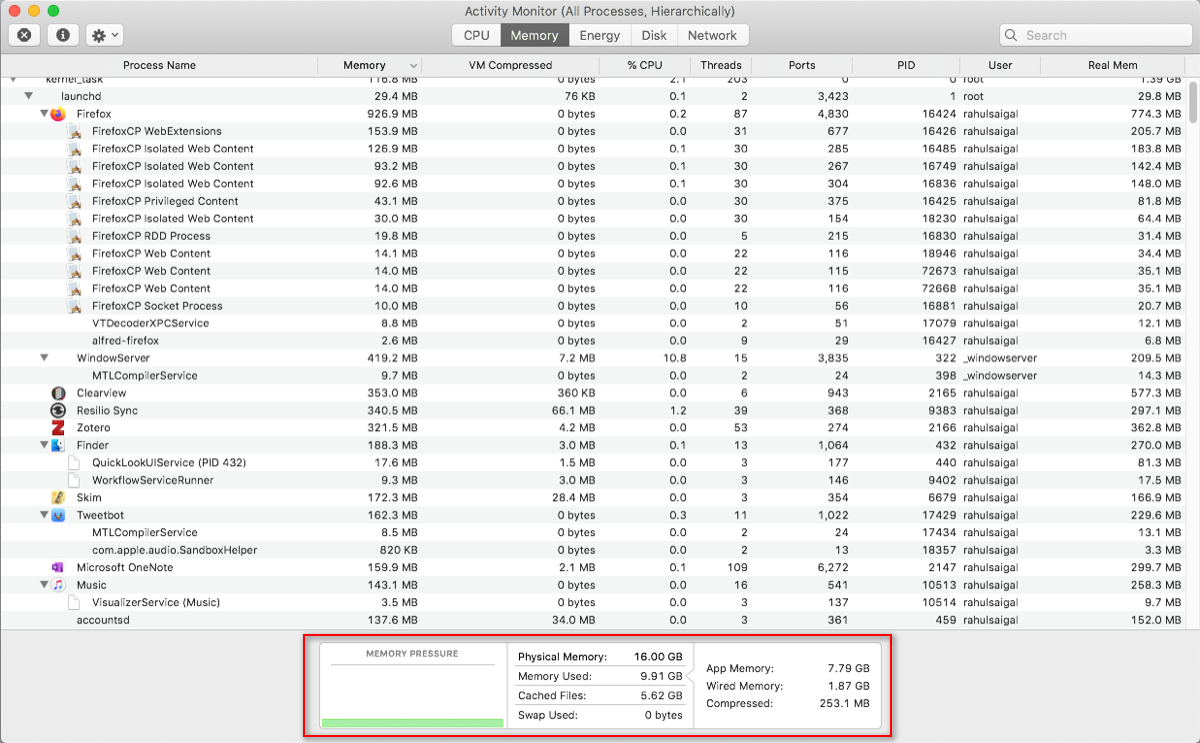
two. The Retentivity Tab in Activity Monitor
The Retentiveness tab displays how much RAM your Mac is using. Along with the CPU, it'southward a main performance indicator of your Mac. At the bottom of the window, you'll see a real-time retentivity graph with values that can assistance you lot diagnose functioning bug.
The Memory Used value is the total corporeality of retentivity used by all apps and system processes. Information technology'due south divided into the following:
- Wired Retentivity: Processes that must stay in retentiveness. They tin can't be compressed or paged out.
- App Memory: Retention allocated to all app processes.
- Compressed: macOS includes software-based memory compression to increase operation and reduce energy use. Your Mac compresses the content used by less active processes to free up infinite for more active ones.
Check if Your Mac Needs More than RAM
The Memory Pressure graph shows the nowadays state of memory resource usage through different colors. Dark-green ways sufficient retentiveness resources are available, while Blood-red ways your Mac has run out of memory and needs more RAM to operate efficiently.
The borderline Yellow is a warning sign. Check to come across if an app is using up retention and causing the memory pressure to increment. If that's the case, quit the app.
View Buried Files Memory Usage
Buried Files is another useful parameter. This tells yous how much retention is presently used by apps, simply is nonetheless available for other apps to have. For example, if you quit Apple Mail later using it for a while, its information will get part of the retentiveness used by cached files.
If you re-launch the Post app, it'll launch faster. Simply if another app needs RAM, macOS will dynamically remove cached data and classify it to other apps.
If Cached Files is consuming a lot of memory, don't fret about it. As long every bit retentiveness pressure level is greenish, it shouldn't be a business. You might demand more than RAM in the futurity but, before that, cheque out some common mistakes that deadening down your Mac. Since Apple silicon Macs take an integrated system on a chip, your only choice is to quit the app.
The Swap Used and Compression Entries
These 2 parameters tell you how much agile process data was swapped out to the startup drive or compressed to save infinite. Compression is preferred to swapping because it makes more room for memory and doesn't slow down your Mac.
A depression number for Bandy Used is acceptable, only a high number indicates that your Mac doesn't have plenty real retention to meet the application demands.
Catching App Memory Leaks
Memory leaks happen when an app doesn't release the allocated memory for reuse. Over time, the leak accumulates and the problematic app comes to a grinding halt. Yous tin hands identify these leaks through Activity Monitor.
three. Review Energy Usage With Activity Monitor
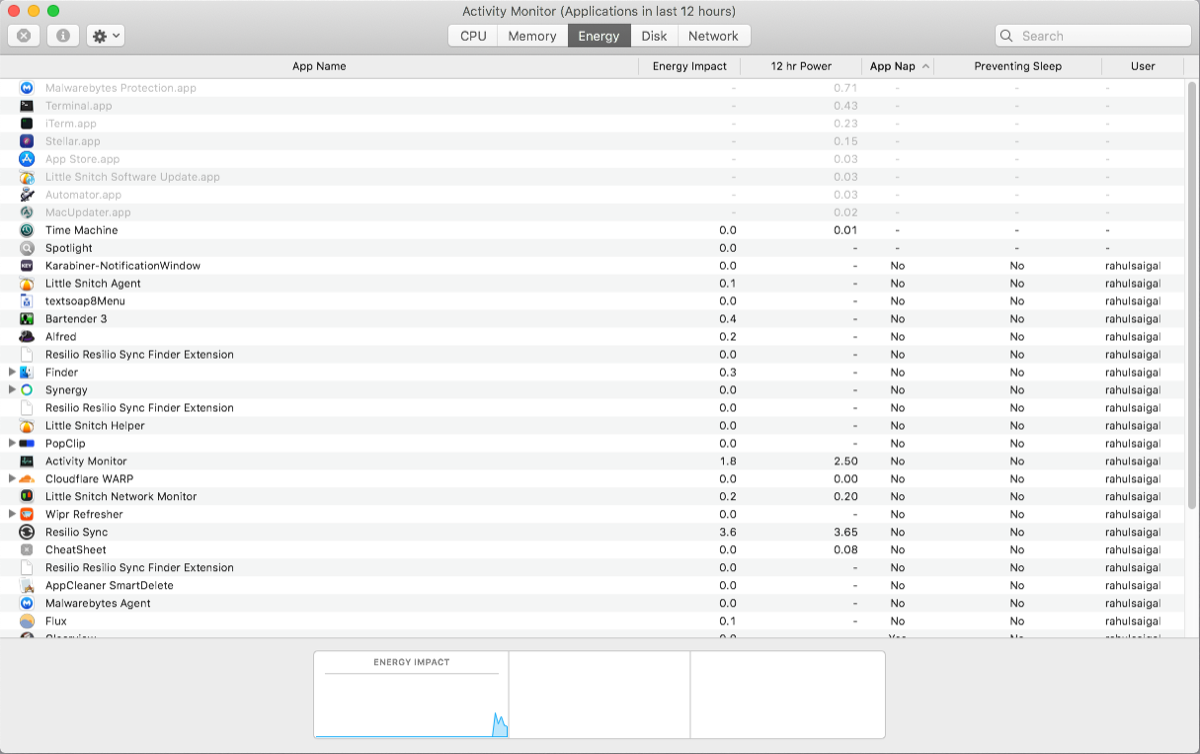
Every MacBook user is likely to accept a valid concern about battery life; you probably want your laptop to run for as long as possible. The Energy pane of Action Monitor is your Mac's resource monitor. It shows overall energy use and power used by each app.
You'll see the Energy Bear upon of running apps, along with the Avg Free energy Impact of each app over the terminal 12 hours or since your Mac booted upward, whichever is shorter. The App Nap feature allows your Mac to put inactive apps to slumber. This field tells yous which apps support this and whether information technology is preventing your Mac from going to sleep or non.
Implications of Energy Usage
The more energy a detail app uses, the shorter your battery life becomes. You should check the Avg Energy Bear upon column to come across which apps use the about energy over time. Quit those apps if you don't need them.
For web browsers, you lot don't have to quit the entire app. Click the triangle side by side to the browser to expand the list of child processes. Observe the one with the highest free energy impact, so forcefulness-quit that process.
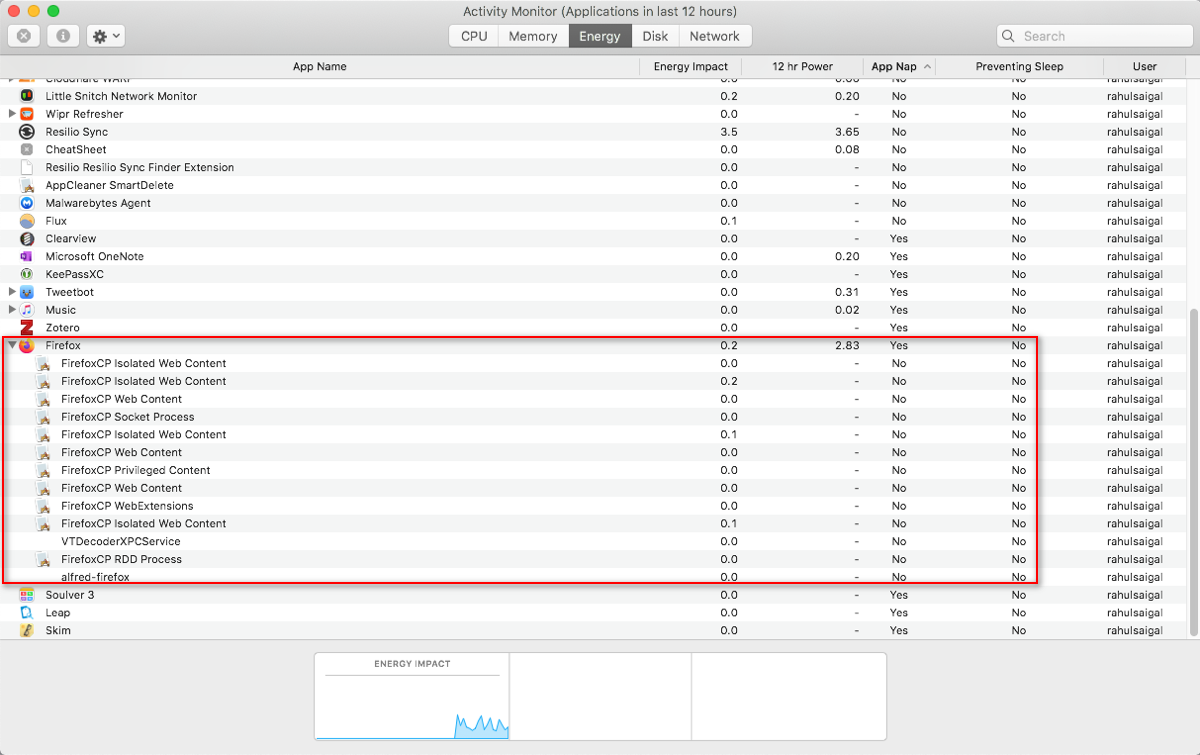
Mostly, those are tabs or plugins that consume significant free energy. If you're using Chrome, cheque out how to control Chrome's retention usage and free up RAM.
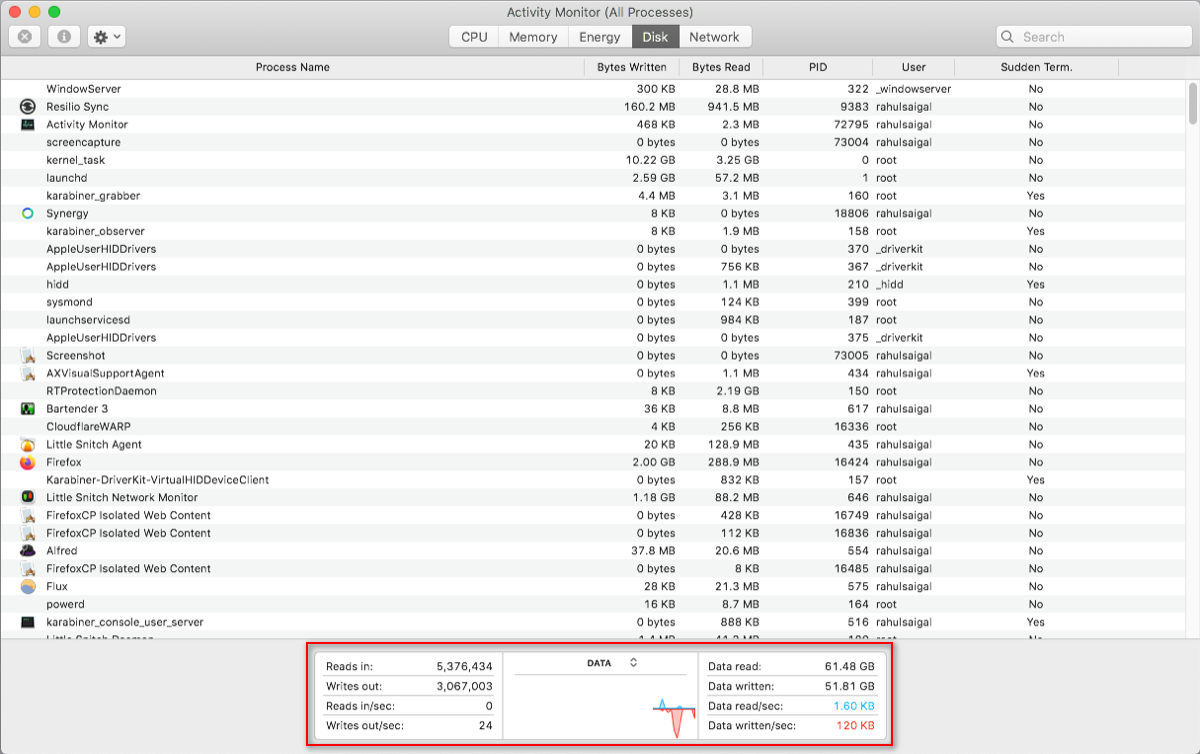
4. Action Monitor's Disk Console
The Disk pane shows the corporeality of information each process has read from or written to the disk. Information technology denotes the number of times your Mac accessed the bulldoze to read (read IO) and write (write IO) data. Blue shows the number of reads per second while scarlet indicates the number of writes per second.
Implications of Disk Activity
Having enough RAM is essential for functioning, but free space on your startup bulldoze is critical for system stability. Pay close attending to the number of reads or writes and observe how your system accesses the read or write data.
If disk activity is loftier, does it correlate with the CPU usage? Some apps or processes can crusade both heavy disk activity and CPU usage, like when you convert video or edit RAW photos. And if your Mac is brusque on RAM, you'll see frequent spikes in deejay activity due to swapping.
5. Using the Network Tab in Action Monitor
The Network pane shows how much data your Mac is sending or receiving over your network. At the bottom, you'll run into network usage in packets and the amount transferred (in reddish) and received (in blueish).
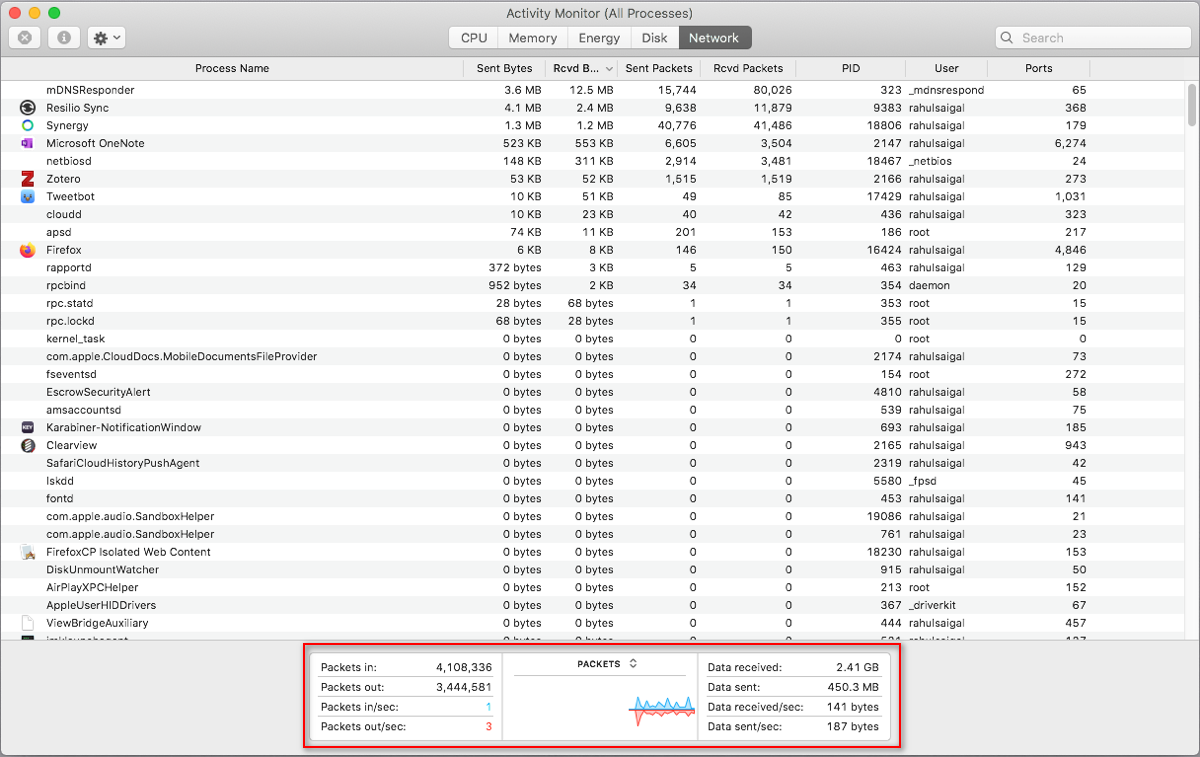
Implications of Network Activity
Some processes naturally generate a lot of network activity, but others using the network a lot might non make much sense. Determining which external resource each procedure is connecting to is a huge pain.
If you're curious to see what information packets are passing through which processes, employ the Petty Snitch app to monitor network traffic on a per-app basis.
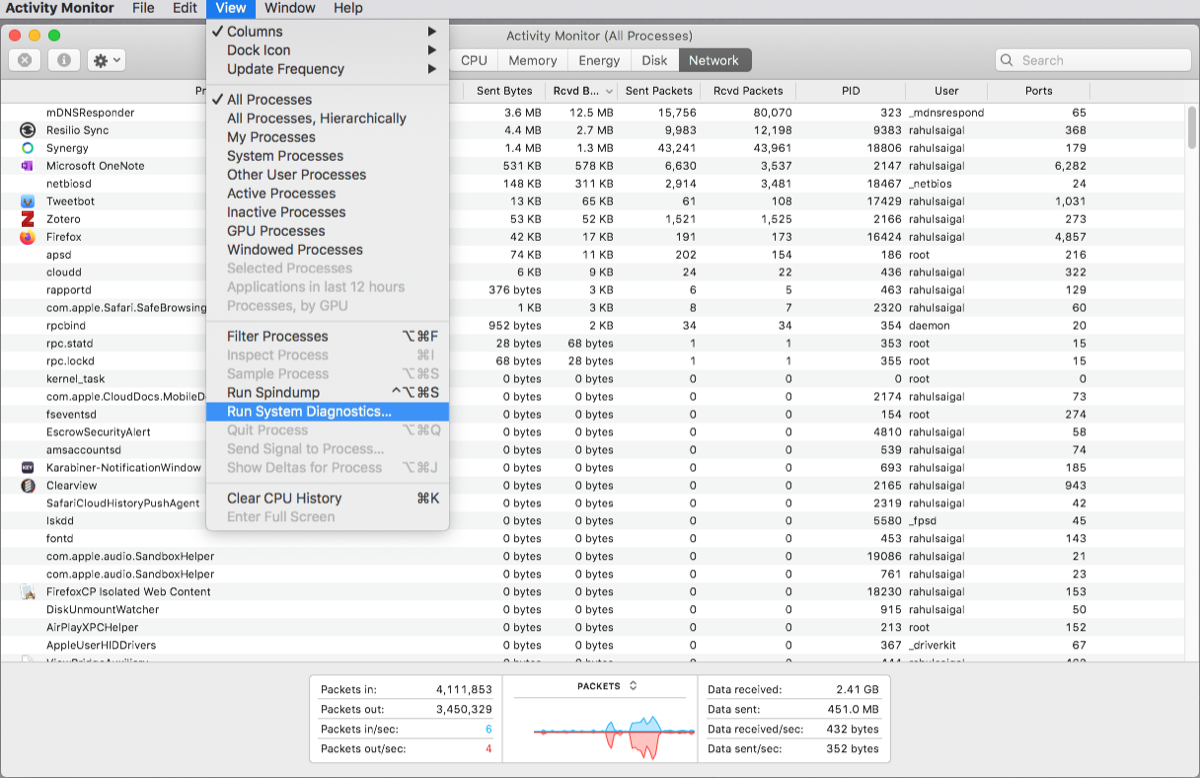
Generate a Arrangement Diagnostics Report
Activity Monitor tin can also help you generate a report virtually the status of your Mac. Yous tin relieve the report and send it to a friend or Apple support for troubleshooting purposes.
To do this, choose View > Organisation Diagnostics. You may need to look a while for this to consummate.
Tune Up Your Mac for the Best Functioning
Activity Monitor is the stock macOS task manager. Past running this tool and following the communication nosotros've covered here, you lot can work out why your Mac is wearisome and what each parameter means to your overall system health.
In one case you take hold of the source of the problem, attempt some tips to tune-upwardly your Mac and make information technology run faster and smoother.
Source: https://www.makeuseof.com/tag/activity-monitor-mac-equivalent-ctrlaltdelete/
Posted by: fosterwhippyraton.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Open Activity Monitor Windows"
Post a Comment